Top 5 Industrial Applications of Stirred Pressure Reactors in 2025
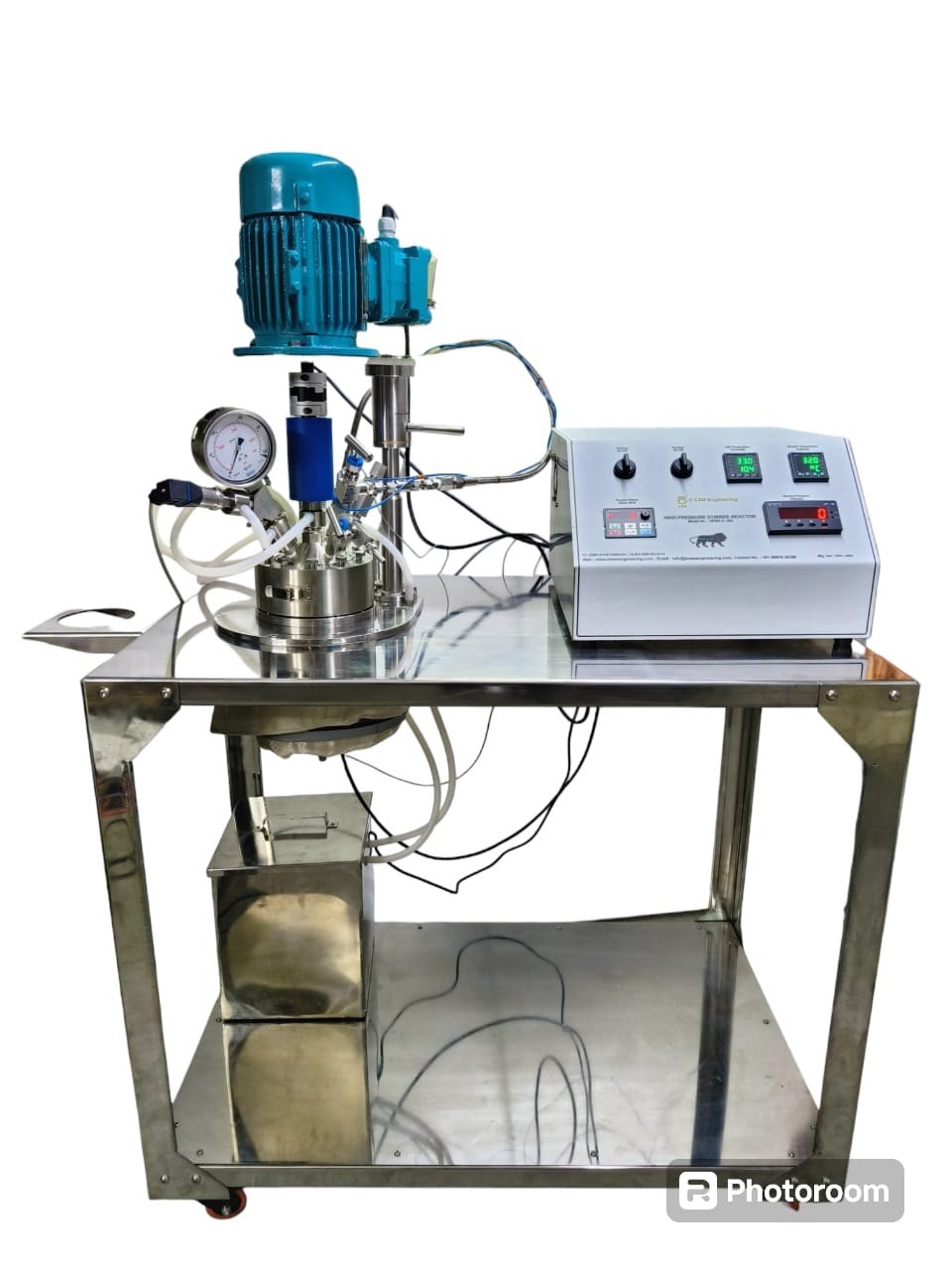

In the world of process engineering, stirred pressure reactors have become essential equipment for industries that rely on precise and consistent chemical reactions under pressure and temperature. These versatile systems provide controlled environments for a range of applications, from research labs to full-scale production lines.
As technology evolves and industrial requirements shift, the role of stirred pressure reactors is expanding. Their importance in chemical synthesis, pharmaceuticals, materials research, and petrochemical processing is only growing stronger in 2025. Below, we take a closer look at five key industrial applications where these reactors are not only used—but relied upon.
1. Pharmaceutical API and Intermediate Manufacturing
One of the largest users of stirred pressure reactors is the pharmaceutical industry. These reactors are critical in the production of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs), where chemical reactions often require high pressure and precise temperature control.
Whether it’s hydrogenation, crystallization, or high-pressure synthesis, stirred autoclaves are used to ensure reactions occur under safe and reproducible conditions. The controlled agitation offered by stirred reactors ensures proper mixing and reaction kinetics, which are essential for purity and batch consistency.
Additionally, pharmaceutical manufacturers often operate in a regulated environment where even minor inconsistencies can result in batch rejection. Here, the precision and repeatability of stirred pressure reactors provide a dependable solution.
2. Specialty Chemicals and Fine Chemical Synthesis
Manufacturing specialty chemicals—such as additives, adhesives, coatings, and surfactants—demands flexible and durable reactor system. Stirred pressure reactors are ideal for these processes, especially when high-pressure or corrosive environments are involved.
In 2025, the market demand for fine chemicals has grown significantly due to developments in electronics, agrochemicals, and energy sectors. With reactions often require controlled environments over extended periods, these reactors help maintain batch uniformity, minimize contamination, and manage thermal performance.
Modern setups allow operators to scale up from laboratory systems to pilot plants without compromising on reaction efficiency, making stirred pressure reactors an indispensable tool in specialty chemical production.
3. Petrochemical and Refinery Catalytic Reactions
Catalytic reactions form the backbone of refining processes, where stirred pressure reactors are commonly used for hydrocracking, reforming, and desulfurization studies. In these high-pressure applications, the reactor’s ability to sustain extreme temperatures and operate safely with reactive gases like hydrogen is critical.
Petrochemical companies use stirred reactors to conduct catalyst testing and scale-up experiments. These systems support reactions involving multi-phase mixtures (gas-liquid-solid), ensuring even catalyst distribution and thorough mixing.
With sustainability becoming a key concern, refineries are also investing in cleaner and more efficient catalytic processes. Stirred pressure reactors play a pivotal role in validating such technologies before plant-level implementation.
4. Hydrometallurgy and Battery Material Development
The push toward electric vehicles and energy storage solutions has led to a surge in battery research and rare earth element processing. Hydrometallurgy—the process of extracting metals using aqueous chemistry—requires equipment that can operate under pressurized and often acidic conditions.
Stirred pressure reactors are now widely used in this field to aid in leaching, precipitation, and other extraction processes. Their ability to handle reactive environments makes them suitable for dissolving metal ores or reclaiming valuable elements from electronic waste.
In 2025, battery companies are also turning to stirred autoclaves to synthesize cathode materials like lithium iron phosphate (LFP) and nickel manganese cobalt (NMC), where controlled temperature and agitation ensure quality particle formation.
5. Polymer and Material Science Research
Developing high-performance materials such as thermoplastics, resins, and composites often starts at the lab scale. Stirred pressure reactors are used to perform polymerization reactions under specific atmospheric and thermal conditions to produce new materials with desirable mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties.
These reactors allow chemists and material scientists to work with monomers and initiators in a closed, pressurized system that mimics production-scale processes. As additive manufacturing and 3D printing technologies expand, custom polymers created in stirred reactors are helping meet the demand for specialized performance materials.
Universities and R&D labs also rely on compact bench-top versions of these systems to carry out exploratory studies before moving into pilot-scale testing.
Advantages Driving Reactor Adoption
Apart from industry-specific applications, the wider adoption of stirred pressure reactors is driven by technological advancements and market needs:
- Real-time monitoring: Integration of digital sensors and data logging systems for pressure, temperature, and agitation speed.
- Improved safety features: Automatic pressure relief systems and robust sealing technology ensure safe operation.
- Versatile configurations: Customizable reactor volumes, materials of construction (SS316, Hastelloy, glass-lined), and agitator designs to suit varied processes.
- Scalability: Easy transition from lab-scale development to pilot and production scale.
These factors combined make stirred pressure reactors a core part of industrial process development today.
Conclusion
As the need for precision, safety, and efficiency grows across industries, stirred pressure reactors remain at the centre of modern chemical and materials engineering. From producing life-saving drugs to developing next- generation battery materials, these systems are play a critical role in shaping industrial progress.
For those in need of reliable high-pressure solutions, Autoclave reactors and related systems continue to evolve to meet the demands of complex applications.